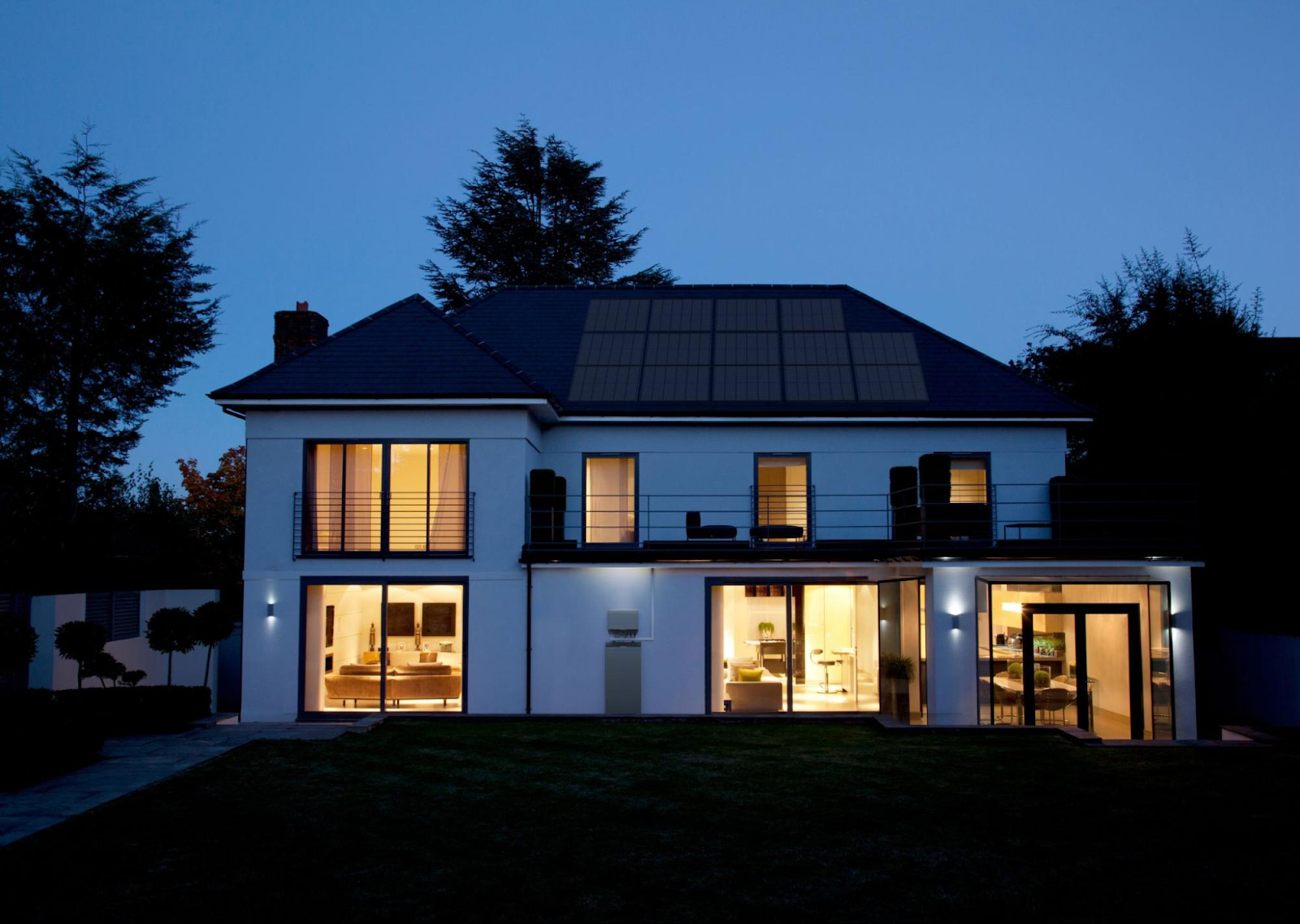
Power outages can strike unexpectedly, leaving homes without electricity for hours or even days. As reliance on electricity grows, having a reliable backup solution is more important than ever. Home battery storage offers an efficient and eco-friendly way to keep essential devices running during emergencies, ensuring peace of mind when the grid goes down.
This article explores how home battery storage UK systems work as an emergency backup, their key benefits, and what to consider before investing. From understanding battery capacity to installation tips, readers will gain valuable insights to make informed decisions and enhance their home’s energy resilience.
What Is Home Battery Storage?
Home battery storage refers to a system that stores electricity for use when needed, typically during power outages or peak energy demand. These systems operate by collecting energy, often from solar panels or the grid, and storing it in rechargeable batteries for later use.
Energy is stored in chemical form within these batteries and converted back to electricity when discharged. Modern systems include lithium-ion or lithium iron phosphate batteries due to their efficiency and durability. Storage capacities can range from a few kilowatt-hours (kWh) to tens, depending on the system design.
Such systems improve energy resilience by providing a reliable backup for essential appliances, like refrigerators and medical devices, during blackouts. They can also store off-peak electricity for use during higher tariff periods, reducing costs while increasing energy independence.
By managing energy consumption and reducing reliance on the grid, home battery storage contributes to more sustainable energy usage in residential settings.
Why Consider Home Battery Storage For Emergency Backup?
The home battery storage system from EcoFlow offers significant advantages during outages and periods of high energy demand. These systems enhance energy control while improving cost efficiency and environmental responsibility.
Benefits Of Emergency Backup During Power Outages
Home batteries automatically switch on when the grid fails, supplying energy for critical devices such as medical equipment, lighting, and refrigerators. This ensures continuity in households reliant on sensitive appliances. UK outages average 0.4 per year and last approximately 35 minutes, making backup crucial in specific situations.
Installing a dedicated consumer unit and earth spike enables seamless operation during outages. This investment supports household safety and convenience in unpredictable circumstances.
Environmental And Economic Advantages
Home batteries store off-peak electricity, enabling usage during peak pricing, cutting annual costs by £200-£500 for a 5 kWh system. They also aid in grid stability by balancing frequency and reducing reliance on fossil fuel power plants.
Each system lowers CO₂ emissions by 1.2-3.5 tons annually. When integrated with solar panels, they further support renewable energy goals, creating long-term environmental and financial benefits.
Types Of Home Battery Storage Systems
Home battery storage systems offer varied options to meet different emergency backup needs. Each type suits specific applications based on cost, lifespan, size, and energy demands.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries dominate residential backup setups. With high energy density and compact design, they efficiently store and deliver electricity. Their fast charging and long lifespan further enhance reliability during outages. The Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO₄) variant is a safer option with greater thermal stability. Maintenance requirements are minimal, and they adapt well to fluctuating temperatures. These batteries can support critical household appliances like refrigerators or medical devices for several hours during power failures.
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries come as flooded, AGM, or gel variants, offering cost-effective short-term backup. Flooded types need periodic water refilling, while AGM and gel versions demand less upkeep. They are heavier and bulkier than lithium-ion options and have a shorter lifespan. Gel batteries perform better in hot climates, resisting temperature-related degradation. Suitable for homes requiring low-budget solutions, they work well for powering less demanding electrical setups during infrequent outages.
Flow Batteries
Flow batteries use liquid electrolytes in dual external tanks and excel in durability. Unlike others, full discharges cause no damage, enabling complete utilisation of stored energy. They offer an exceptional number of charge-discharge cycles but come with large space requirements and significant upfront costs. These characteristics make them more practical for large-scale use in commercial or agricultural settings rather than typical residential applications.
Key Features To Look For In Battery Storage Systems
Home battery storage systems must be evaluated on features that determine their performance during outages. These features impact reliability, energy delivery, and compatibility with existing setups.
Battery Capacity And Output
Capacity defines how long a battery can supply energy, while output measures the power delivered at once. A 5 kWh battery, for example, may keep lights, a refrigerator, and internet equipment running for several hours. Higher capacities extend energy availability but increase cost.
Output capacities of around 3-10 kW often support small to medium households during outages. Systems prioritising essential circuits use energy more efficiently, as they only target critical devices rather than powering the entire property.
Lifespan And Efficiency
Battery lifespan affects long-term value, with most lithium-ion batteries completing 3,000-5,000 charge cycles, or over 10 years in residential use. Efficiency measures the energy retained and converted for use, with values often exceeding 90%.
Lower-quality batteries waste more stored energy through inefficiencies. Lithium-iron phosphate batteries last longer than standard lithium-ion, often exceeding 6,000 cycles. High efficiency reduces energy losses, boosting overall performance.
Compatibility With Solar Panels
Many systems recharge using solar panels, enhancing backup availability during grid failures. Pairing batteries with solar panels stores excess daytime energy for reuse later. Configurations often include inverters and transfer switches to isolate the home safely during outages.
Some setups prevent loss by directly charging batteries from solar panels when the grid is down. Homes with these systems gain reliability and energy independence, especially where outages are frequent or extended.
Installation And Maintenance Insights
Installation Process
Installing a home battery system involves evaluating energy use, selecting a suitable system, and professional setup. Identifying energy demands starts the process, considering household size, appliances, and peak usage.
The battery system must integrate seamlessly with existing electrical setups or solar installations. Licensed technicians connect the system to the home’s electrical network, ensuring adherence to safety standards. Updates to electrical wiring or circuit components might sometimes be necessary. Specific inverter types may permit battery charging with solar energy during outages.
Regular Maintenance Tips
Consistent care keeps home battery systems reliable and effective. Visual checks identify wear or physical damage, preventing larger issues. Built-in monitoring tools help track capacity and performance levels.
Users are advised to clean components within the manufacturer’s guidelines and arrange yearly professional servicing. Technicians inspect connections, test system functionality, and prolong operational health. Batteries, depending on type and use, require replacement every 5 to 10 years to maintain optimal backup reliability.
Cost Considerations And Incentives
Upfront Costs And Long-Term Savings
Home battery storage systems come with initial costs that vary between £3,000 and £10,000, based on the size and technology involved. Larger capacity batteries typically increase the upfront expense. Installation charges form part of this total, requiring professional setup.
Although the initial cost can feel steep, the savings over time really add up. A 5 kWh battery can shave about £200–£500 off your annual electricity bill. And if you charge it during off-peak times, like with Economy 7, you get the most out of cheaper electricity and don’t have to rely as much on expensive power during peak hours.
Government Incentives And Subsidies
Current government incentives significantly lower the financial barrier for home battery storage in the UK. A 0% VAT rate applies to battery storage, cutting purchase costs by 20%, effective until 31 March 2027.
On top of VAT relief, there are grants that can help make home batteries more affordable. They’re usually aimed at certain groups and have a few rules to qualify, but they make it easier for more people to get on board. These incentives don’t just save money—they also help more households take part in the move toward renewable energy.
Potential Drawbacks And Limitations
High upfront costs represent a significant barrier to adopting home battery systems. Installation and equipment expenses can range from £3,000 to £10,000. Despite falling prices and financial incentives, the initial investment remains steep for many households.
Storage capacity constraints limit these systems’ ability to power an entire home. Smaller systems often reserve energy for essential devices, such as refrigerators or medical equipment, during power outages. Extended interruptions highlight this restriction.
Battery lifespan is finite, often requiring replacement every 5 to 15 years. Replacement costs and potential performance decline over time add to long-term expenses. Regular monitoring and servicing are necessary to prevent premature deterioration.
Dedicated installation space is another requirement. Batteries occupy physical areas of varying dimensions and may need ventilation to maintain safety and efficiency. Limited space in urban homes can complicate installation.
Environmental concerns arise during manufacturing and disposal. Extracting materials like lithium impacts ecosystems, while improper disposal creates waste management challenges.
Conclusion
Home battery storage offers a practical and eco-friendly solution for maintaining energy resilience during emergencies. By ensuring critical devices stay powered and reducing reliance on the grid, these systems provide both peace of mind and long-term savings.
While upfront costs and space requirements may pose challenges, the benefits of enhanced energy control, cost efficiency, and reduced carbon emissions make them a valuable investment. With advancements in technology and supportive incentives, adopting home battery storage is becoming more accessible for households aiming to secure reliable backup power and embrace sustainable energy practices.
Stay in touch to get more updates & alerts on Baddieshub! Thank you