Sheet metal drawing is a basic manufacturing process used throughout various industries to shape metal without altering its structure. In addition to forming, drawing is a significant part of the processes used when fabricating parts in the automotive, aerospace, electronics and appliance sectors.
The sheet metal process allows it to be formed into lightweight, durable, and high-performance components. In this article, we will master sheet metal drawing, including its process, advantages, and applications.
What Is Sheet Metal Drawing?
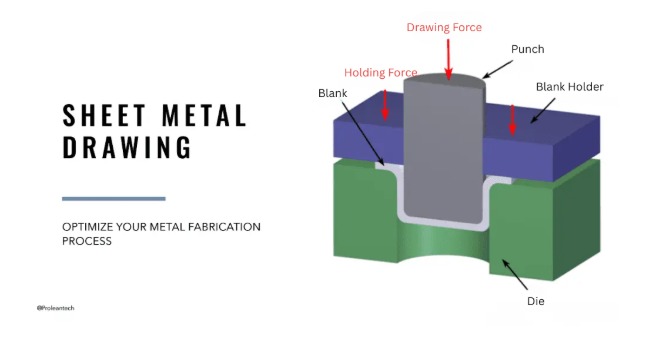
Sheet metal drawing is a metal forming process in which a flat sheet of metal is made into a three-dimensional shape through the use of tensile forces. This process does not involve cutting or machining; rather, it includes changing shape without losing any material. Usually, the sheet metal is secured around the edges and is either pushed into or pulled over a die by the application of a die punch. The metal flows plastically while assuming the shape of the die.
The goal of sheet metal drawing is to create hollow, cup-shaped contour shapes from a flat sheet of metal with minimum wrinkling or tearing.
Drawing Manufacturing Process
The drawing manufacturing process includes steps and considerations.
Blanking: A flat sheet of metal is cut to the size needed.
Clamping: A blank must be clamped using a blank holder or die so that it cannot be excessively compressed.
Punch: A punch is applied, punching the sheet that forms the shape.
Material Flow: The material is completely flowing and stretching into the die shape without breaking.
Trimming & Finishing: The extra material is trimmed, and the part may be cleaned or coated.
Choosing the right material is very important. Some commonly used metals are aluminum, steel, stainless steel, copper, and brass. Make sure the material has proper characteristics such as ductility, strength, and corrosion resistance.
Forming Drawing Vs Sheet Metal Drawing
Forming drawing is a term that includes many other processes, such as bending, stretching, stamping, and drawing. In contrast, sheet metal drawing only refers to the process of drawing a sheet into a hollow shape through tensile stress. Therefore, sheet metal drawing is a type of forming drawing, but not all processes of forming involve drawing.
Deep Drawing Sheet Metal
Deep Drawing is a type of sheet metal drawing in which the depth of the formed part is greater than the diameter. Many products are made from this method, such as beverage cans, kitchen sinks, saucers, fuel tanks, and automotive body panels.
Characteristics of Deep Drawing:
- The material is considerably stretched.
- Requires a strong punch and die system.
- Often requires multiple stages or multi-pass operations when producing parts with high depths.
- Careful control of the black holder force is important to prevent wrinkling and balance against tearing, and thinning as well.
Deep drawing sheet metal processes are extremely automated in modern manufacturing and often involve computer-aided design and CNC machining.
Metal Drawing Process: Key Factors and Tools
In the metal drawing process, the actual successful operation depends on.
- Punch and Die: Components must be designed and manufactured accurately and aligned.
- Lubrication of the tooling: Provides lubrication and minimizes the friction of metal against the tooling, as well as prevents excess tool wear or drawing defects.
- Ductility of the material: It is a measure of how deformable the metal is before fracture.
- Drawing Ratio: This is simply the size of the blank diameter to the size of the punch diameter. The larger the ratio, the greater the deformation of the blank.
- Blank Holder Force: Blank holder force is needed to hold the material around the edges to prevent wrinkling of the material while it is being drawn.
Drawing Manufacturing Applications
The drawing manufacturing process is widely used in all industries.
Automotive Industry:
- Fuel tanks
- Car doors
- Body panels
- Engine parts
Aerospace:
- Wings Section
- Satellite parts
- Housing for engines
Consumer Goods:
- Kitchen sinks
- Cookware
- Metal furniture
Electronics
Connectors
Covers
In short, sheet metal drawing allows for high-precision mass production of components with good repeatability, which is important for today’s manufacturing.
Advantages of Sheet Metal Drawing
1 Material Efficiency: Minimal or no material waste
2 High Strength: Drawn parts usually have higher mechanical strength from work hardening.
3 Lightweight Construction: It’s useful for aerospace and automotive processes that benefit from weight reduction.
4 Cost Effective; Low cost per part when tooling is developed and manufacturing is ramped up.
5. Consistency: It enables the manufacture of consistent, uniform parts.
Limitations and Challenges
While there are advantages to sheet metal drawing, there are many challenges.
Tooling Costs: The initial cost of designing precise dies and punches can be expensive
Material Limitations: Not all metals exhibit good ductility, which limits deep drawing
Defects: Improper control of process parameters results in defects such as tearing, earing, or wrinkling
Springback: Springback of the metal after deformation must be considered in design.
Sheet Metal Drawing Trends
Sheet metal drawing will continue to develop as technology progresses. The integration of automation and robots into industrial drawing processes will reduce lead time and costs, while maintaining product quality in a fast and precise manner.
Additionally, additive manufacturing processes, including 3D printing, will be integrated with traditional sheet metal drawing processes, with the possibility of hybridization. Sustainability will drive the development of new sustainable materials and processes for sheet metal drawing for environmental savings, achieving less waste, energy, etc.
Conclusion
Sheet metal drawing is still a foundation for contemporary metal forming. It is an established and efficient way to create hollow and contoured shapes, with variations like deep drawing and form drawing to serve the industries that require strength and precision. As automated, simulation, and other technologies progress, the future of the metal drawing process becomes more streamlined, sustainable, and flexible.
Through understanding the guiding principles, tools, and applications of the drawing manufacturing process, manufacturers can take advantage of those fundamental processes to improve product designs, reduce waste, and improve production efficiency.
Stay in touch to get more updates & alerts on Baddieshub! Thank you